MAPS™ GPRS Gb Interface Emulator
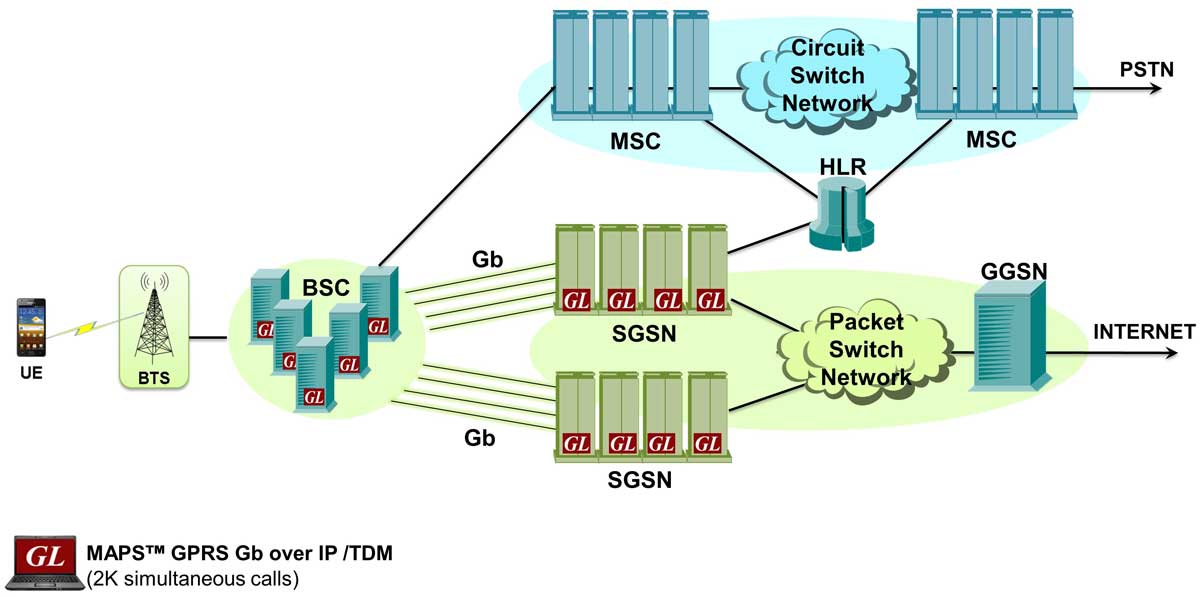
Simulation of GPRS Gb interface connecting BSS (Base Station Subsystem) and SGSN (Serving GPRS Support Node) network elements handling PS mobile traffic.
Brochure Request a Demo / QuoteOverview
GPRS, or General Packet Radio Service, was introduced (in the late 90's and early 2000's) to enhance data carrying capabilities of the basic GSM Network. Initially it used the conventional T1 E1 transport and frame relay protocol. Also as the wireless infrastructure evolved towards IP, the migration of 2G systems to IP interface provided many advantages including increased throughput, capacity, and economy.
To permit our customers to emulate, test, and verify GPRS Gb over IP, GL offers MAPS™ GPRS Gb (PKS131), a multi-protocol, multi-technology platform that also supports many other protocol families including TDM, IP, ATM, and Wireless.
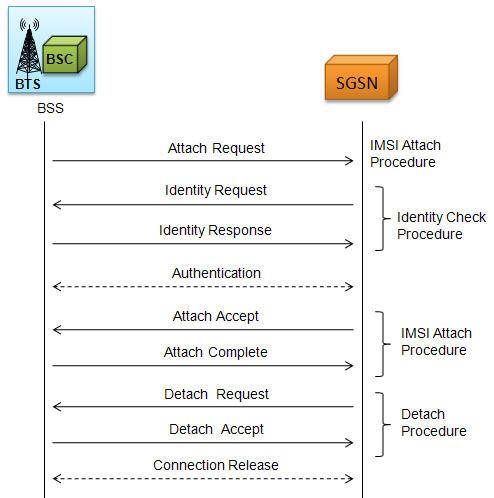
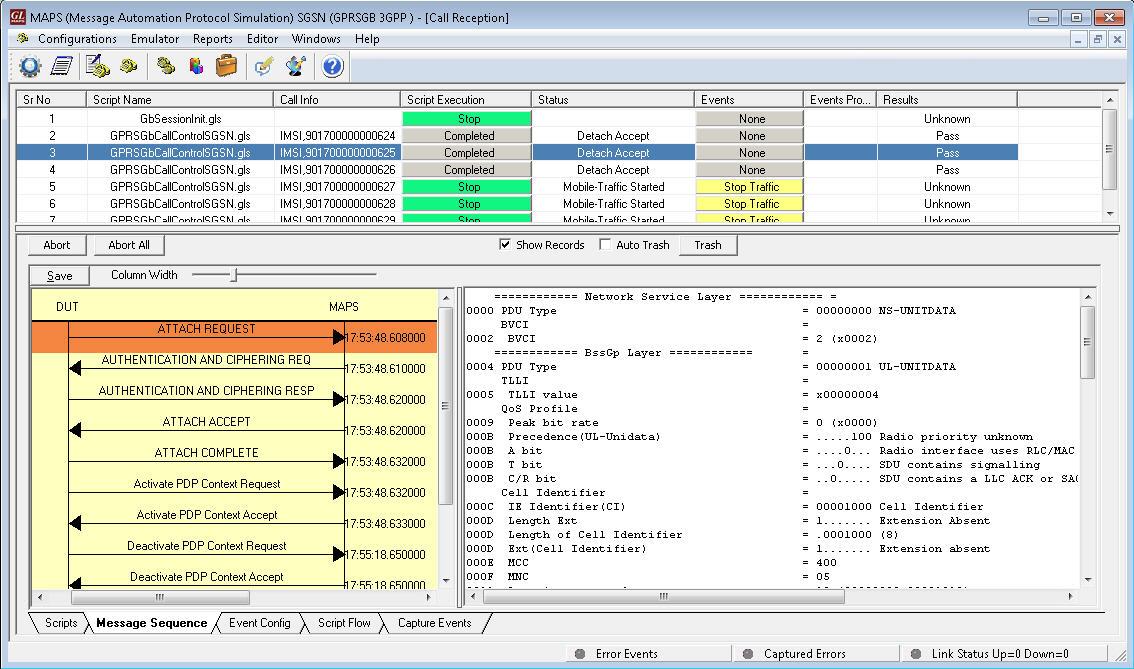
MAPS™ GPRS Gb supports simulation of BSS (Base Station Subsystem) and the SGSN (Serving GPRS Support Node) network elements over IP transmission protocol. Besides testing network elements (SGSN and BSS), the tester also involves error tracking, regression testing, and load testing/call generation. MAPS™ GPRS Gb interface Emulator supports various procedures including Network Service Control, Identity Check, Combined GPRS / IMSI Attach, and Routing Area Update. It can run pre-defined test scenarios against the interface test objects in a controlled and deterministic manner.
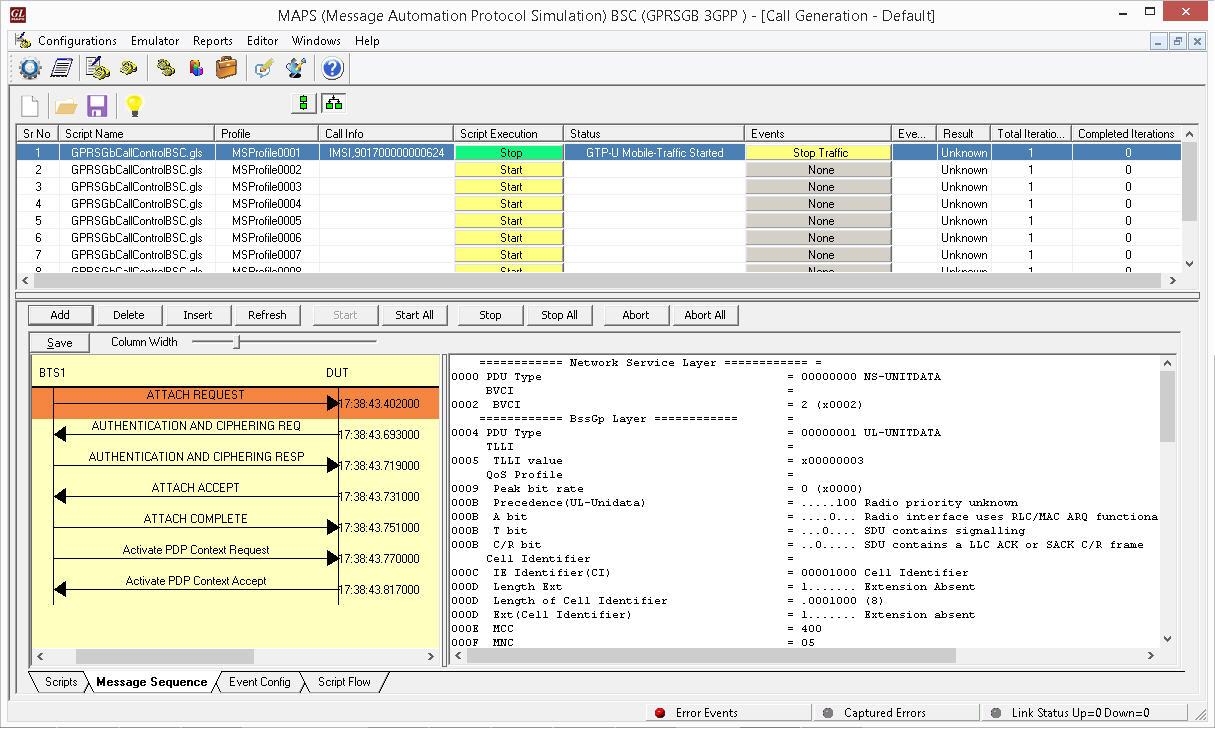
MAPS™ GPRS Gb Interface Emulator supports powerful utilities like Message Editor, Script Editor, and Profile Editor which allow new scenarios to be created or existing scenarios to be modified as per the protocol standards listed in the table below.
MAPS™ GPRS Gb supports ETH103 - Mobile Traffic simulation over Gb interface between BSC and SGSN. Currently, this module transmits the pre-canned HTTP file (*.txt) between BSC and SGSN nodes. It multiplexes both signaling and traffic over Gb interface.
By mimicking real-world customer behavior in lab environments, our solutions allow mobile operators and equipment manufacturers to verify their wireless networks before deployment. In other words, one can setup a virtual real-time network simulating all the network elements using “MAPS 2G Wireless Lab Suite”. The test suite supports simulation of Gprs Gb, Gn Gp, and other interfaces in GPRS network required to simulate PS data traffic.
GL also provides an independent GUI based GPRS protocol analyzer -TDM (optional application – XX155) and GPRS protocol analyzer – IP (optional application – PKV103) for online capture and decode of the signaling in real-time and as well as offline.
Key Features
- Setup a virtual real-time network simulating 2G-GSM GPRS network elements using ‘MAPS™ 2G Wireless Lab Suite’
- Simulates SGSN (Serving GPRS Support Node) and BSS (Base Station Subsystem) elements in GPRS Gb interface over IP
- Simulates Control plane Gb mode
- Generates hundreds of Control Signaling (Load Testing)
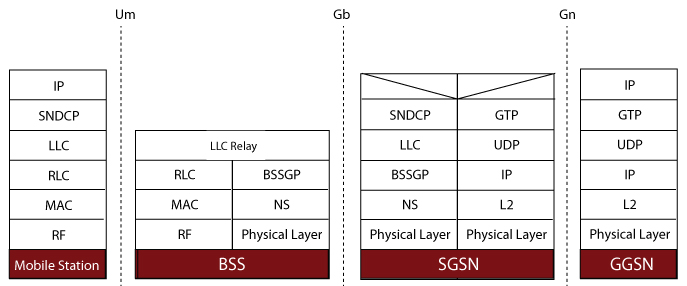
- Generates and processes NS (Network Service), BSSGP (Base Station Subsystem GPRS Protocol), and various GPRS session procedure messages
- Supports Gb interface procedures including Network Service Control, Identity Check, Combined GPRS / IMSI Attach, and Routing Area Update
- Insertion of impairments to create invalid messages
- Supports GTP Traffic (GTP User Plane Data) which includes: verification like BERT testing, HTTP traffic generation capability, GGSN can actually be connected to real IP network to simulate Gateway testing
- Supports customization of call flows and message templates using Script and Message editors
- Supports scripted call generation and automated call reception
- Provides Call Statistics and Events Status
- Automation, Remote access, and Schedulers to run tests 24/7
Applications
- Complete analysis and simulation capability
- Provides fault insertion, and erroneous call flows testing capability
- Functional testing, Regression testing and Conformance testing of network elements
- Ready scripts makes testing procedure simpler, less time consuming and hence time to market products
- QoS requests for greater or lesser bandwidth
- GSM GPRS lab setup can be used in educational institutions for training purposes
Supported Protocols Standards
|
|
|||||||||||||||
Call Simulation over GPRS Gb
The MAPS™ GPRS Gb Interface Emulator simulates various GPRS procedures over IP between the SGSN (Serving GPRS Support Node), and BSC (Base Station Controller) nodes.
Resources
Please Note: The XX in the Item No. refers to the hardware platform, listed at the bottom of the Buyer's Guide, which the software will be running on. Therefore, XX can either be ETA or EEA (Octal/Quad Boards), PTA or PEA (tProbe Units), XUT or XUE (Dual PCIe Express) depending upon the hardware.
| Item No. | Item Description |
| PKS131 | MAPS™ Gb Emulator over IP for BSC & SGSN |
| ETH100 ETH101 ETH102 ETH103 |
Mobile Traffic - PacketCheck™ Mobile Traffic Core - GTP Mobile Traffic Core - Gateway Mobile Traffic Core - Gb |
| Related Software | |
|---|---|
| XX155 | GPRS Protocol Analyzer |
| OLV155 | Offline GPRS Protocol Analyzer |
| PKS166 | MAPS™ UMTS - Gn Gp Interface Emulation |
| PKS137 | MAPS™ GSM A Emulation over IP |
| XX692 | MAPS™ GSM A Interface Emulator |
| XX647 | MAPS™ ISUP Conformance Test Suite (Test Scripts) |
| XX648 | MAPS™ ISDN Emulator |
| XX649 | MAPS™ ISUP Emulator |
| XX693 | MAPS™ GSM Abis Interface Emulator |
| XX120 | SS7 Analyzer Software |
| OLV120 | Offline/ Remote SS7 Analyzer Software |
| XX150 | T1 or E1 Real-time GSM Protocol Analyzer |
| OLV150 | Offline T1 or E1 GSM Protocol Analyzer |