GL Enhances End-to-End Wireless Network LAB Solutions
6th, Oct 2017
Welcome to October 2017 issue of GL Communications' Newsletter providing information and insight into our enhanced End-to-End Wireless Network LAB Solutions (2G, 3G, 4G and IMS). GL’s 3G and LTE Lab Solution is enhanced to support Voice, Video and SMS calls with roaming User Equipment (UE) in the network.
Overview
GL's MAPS™ Wireless Lab Suite (2G, 3G, 4G, IMS) along with radio access elements is used to provide an advanced full-fledged network environment that enables user to test their applications, devices, and services on simulated wireless infrastructure environment prior to deployment on a real-time network. The wireless lab test suite is an invaluable tool for protocol characterization and testing, performance measurement, and training.

The test suite can be used to simulate all or specific elements within wireless networks infrastructure using simple ready-to-use test bed setups. The test systems allow for simultaneous execution of various test cases across networks. It also allows for performance and conformance testing compliant with 3GPP standards.
Enhancements
A recent enhancement to MAPS™ Wireless Lab Suite (2G, 3G, 4G, IMS) includes ability to simulate Roaming procedures across 3G and 4G networks. Roaming 3G/4G UEs ensures that a traveling wireless device (typically a cell phone) is connected with the network continuously without losing the connection.
With GL’s Wireless Network Lab, you can simply simulate Roaming 3G/4G UEs and test certain functionalities by automatically placing and receiving voice calls, send and receive data, or access other services, when travelling within or out of the geographical coverage area of the network. Real mobile phones can also be used with GL’s Wireless Network Lab suite to create a real-time Wireless Network Environment.
New test scenarios added to GL’s Wireless Network Lab Suite -
- VoLTE (SIP) call between two LTE UEs in same network or different networks
- CSFB Voice and SMS from a roaming LTE UE and a roaming UMTS UE
- SMS sent from a roaming 3G UE to a roaming LTE UE
- Use of CAMEL for SMS and prepaid calls
The test scenarios that can be simulated using GL’s Wireless Network Lab Suite are discussed further below
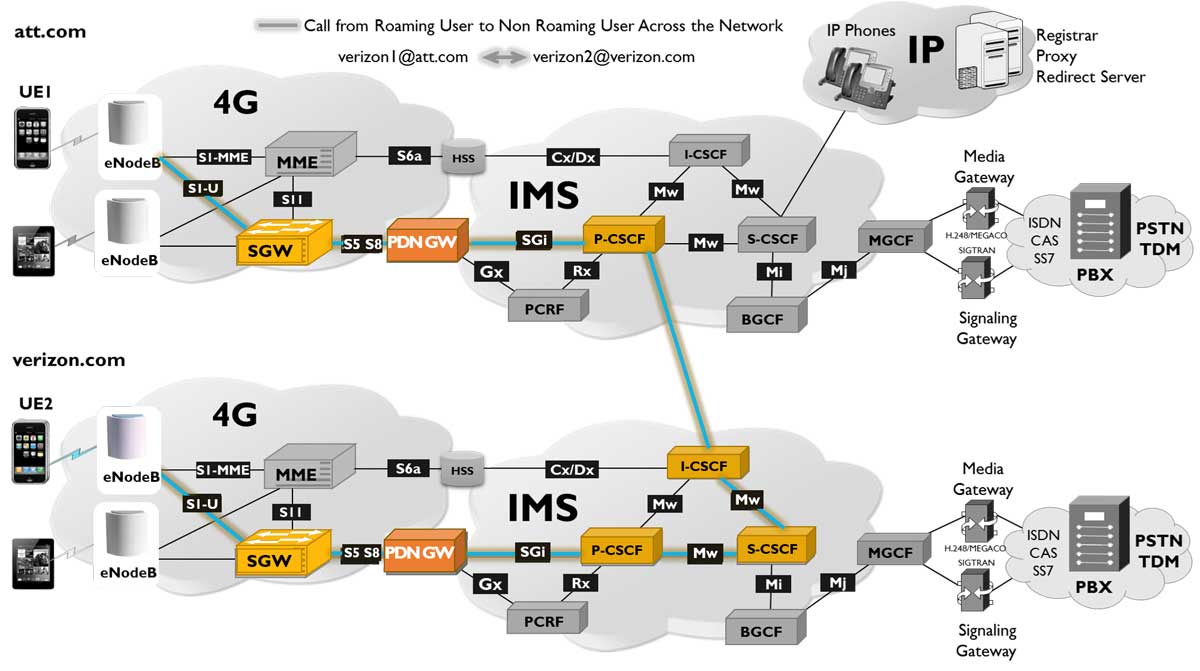
VoLTE (SIP) call between two LTE UEs roaming and non-roaming scenarios
MAPS™ 4G IMS Wireless Lab can simulate various nodes in the LTE IMS network, interacting with each other facilitating a VoLTE call. In the following lab test scenario, two LTE enabled UEs are used to establish a VoLTE call via MAPS™ 4G Wireless and IMS Lab.
The LTE/IMS network involves, IMS call session control function (CSCF), simulating distinct elements such as the Proxy CSCF (P-CSCF), the Interrogating CSCF (I-CSCF), and the Serving CSCF (S-CSCF) in the IMS network. Each of the nodes can be configured using GL’s MAPS™ capable of simulating functionalities of each node in the network.
End-to-End call flow through various network elements can be verified to understand the entire process or you could just replace one of the network elements with that of operators’ and verify its functionality.
CSFB Voice and SMS from a roaming LTE UE and a roaming UMTS UE
Circuit switched fallback (CSFB) is a technology devised to allow Voice services. LTE doesn't support circuit switched calls because LTE is packet only technology.So, when a LTE device is used to place a voice call or send SMS, the device "falls back" to the 3G or 2G network to complete the call or to deliver the SMS.
The SGs Application Part (SGsAP) is used on the SGs interface between the Mobility Management Entity (MME) in the EPS and the Visitor Location Register (VLR). It allows location management co-ordination and relay certain messages related to GSM circuit switched services over the EPS system.
The following lab setup realized using the MAPS™ 4G 3G Wireless Lab to simulate both 3G and LTE User Equipment (with registered SIMs) and entire wireless infrastructure to generate the Voice/SMS traffic from LTE UE and traverse through CS network. This setup illustrates interworking between VLR/MSC and MME over SGs, where CSFB calls are initiated between a roaming LTE UE and a roaming UMTS UE.
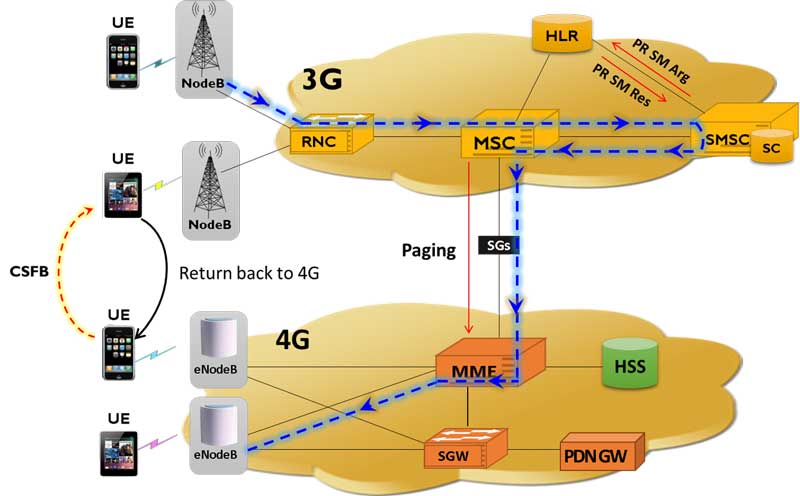
Figure: CSFB from 4G to 3G for voice and SMS
Use of CAMEL for SMS and Prepaid Calls
The CAMEL Application Part (CAP) information flow is defined between functional entities such as Service Control Function (SCF) and Service Switching Function (SSF) distributed across the GSM, GPRS, and UMTS networks. The capability of CAMEL Application Part (CAP) is defined by means of ‘operations’, which means one entity, starts a procedure in the peer entity. The Service Control Point (SCP) is the main entity that control IN services.
As depicted below in the lab setup diagram, GL’s MAPS™ CAMEL IP Emulator can be configured as SCF and SSF entities emulating CAP supplementary services such as unified messaging, and prepaid calls. For example, CAP controls SMS as a subscribed service, establishes relationship between the MSC and the gsmSCF. Initial DP SMS (IDP-SMS) operation is used to start the CAMEL service. The prepaid voice call procedure specifies the charging related information to be provided by the SSF and the conditions on which the information should be reported back to the SCF.
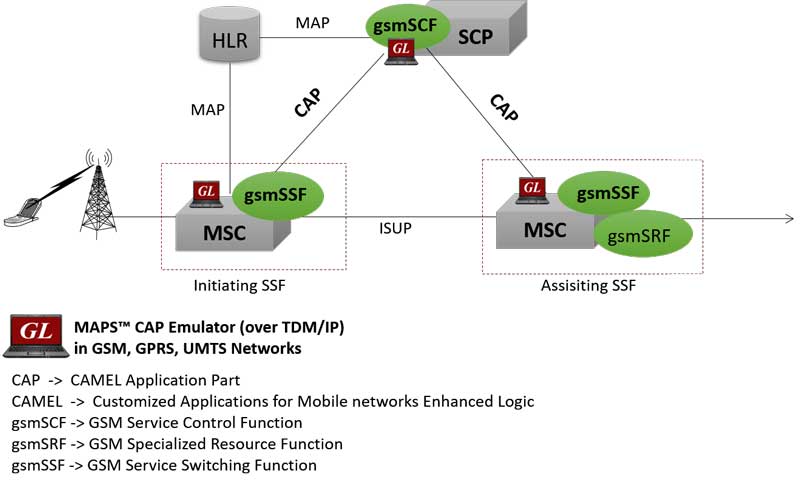
Figure:CAMEL Application Part for Controlling Supplementary Services
Important Features
- Perform end-to-end testing across any network, Mobile-to-Mobile, Mobile-Landline, and Mobile HTTP Web Access simulation
- Setup a virtual real-time network simulating all the network elements provided in the architecture
- Any of the network elements in the above architecture can be replaced with user's DUT to perform single interface, multi-interface, or wrap-around testing
- Circuit switched traffic can be generated and recorded using RTP application
- Perform end-to-end testing supporting HTTP Web Access simulation
- Supports Circuit Switched Fallback scenario
- Supports simulation of Roaming Scenarios
- Supports VoLTE call simulation
- Supports call between users in different networks
- Supports SMS through SGs interface
- Supports SMS over IMS
- Supports IPSec, TLS and SRTP
- Supports simulation of Invalid scenarios
- Supports Bulk calls simulation
- Supports PDF report generation
- Supports Impairing the protocol messages
- Supports detailed statistics and user defined statistics
- Graphical representation of Calls per second, and maximum simultaneous calls
 Back to Newsletter Index Page
Back to Newsletter Index Page