GL Releases MAPS™ SLs Emulator
for Simulation of Location Based Services in LTE Network
11th, May 2018
Welcome to another May 2018 issue of GL Communications' Newsletter. The following newsletter discusses LoCation Services (LCS) architecture in LTE network briefly, and GL’s latest MAPS™ SLs Emulator solution to meet the requirements in location services testing on LTE networks.
LCS Architecture in LTE - Overview
The LCS architecture in LTE is similar to GSM/UMTS network and follows a client/server model with the positioning functionality distributed across LTE radio nodes, eNodeBs (eNB), Mobile Management Entity (MME), Evolved-Serving Mobile Location Center (E-SMLC) and Gateway Mobile Location Center (GMLC).
As depicted in the diagram, some of the important interfaces participating in the location request and response in LTE network are summarized below -
- SLs interface - MME is accessible to the E-SMLC via the SLs interface using LCS-AP protocol
- SLg interface - MME is accessible to the GMLC via the SLg interface using Diameter protocol
- SLh interface - HSS is accessible to the GMLC via the SLh interface using Diameter protocol
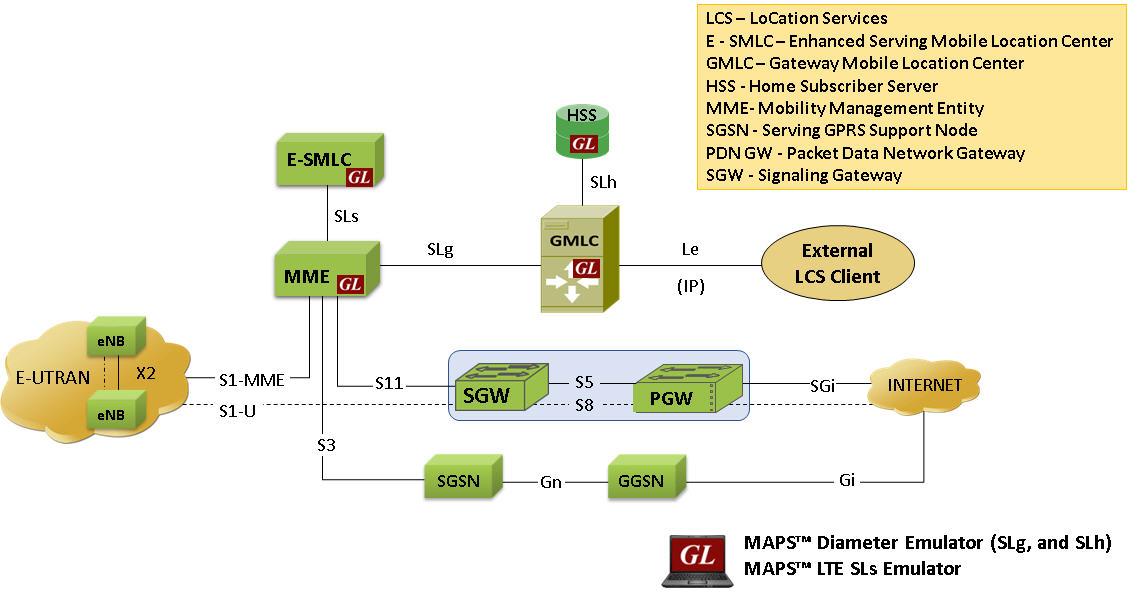
LoCation Services (LCS) E-UTRAN Network Architecture
LPP protocol supports hybrid positioning method, in which two or more position methods are used simultaneously to provide accurate measurements. The LTE Positioning Protocols (LPP and LPPa) are carried in LCS-AP PDUs over established SCTP session between an E-SMLC and MME.
Location estimation uses hybrid positioning methodologies from the list of positioning methods given below. These positioning methods may be UE-based, network-based, UE-assisted, network-assisted and/or combination of these methods. The main difference is that the network-based measurements do their calculations at the infrastructure, while the UE based measurements do their calculations at the device.
The standard positioning methods used in LTE network are:
- Enhanced Cell-ID (network based, handset assisted)
- OTDOA positioning method (network based, handset assisted)
- UTDOA positioning method (network based)
- A-GNSS based positioning methods (handset based, network-assisted)
For further details on positioning methods, refer to User Equipment (UE) positioning in E-UTRAN.
Simulation of LCS SLs interface using MAPS™
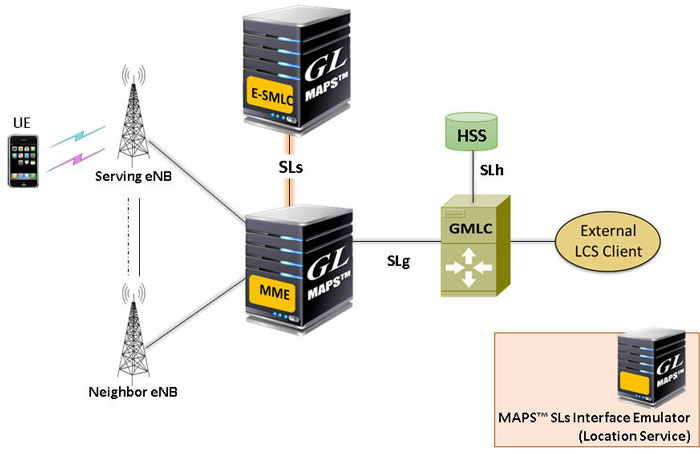
MAPS™ simulating SLs interface
The figure above shows the architecture applicable to the positioning of a UE with E-UTRAN access. The SLs interface is used to convey LCS-AP (LCS Application Protocol) messages and parameters between the MME to the E-SMLC. It is also used for tunnelling LTE Positioning Protocols (LPP between the E-SMLC and the target UE), which is transparent to the MME as described in 3GPP TS 36.305.
MAPS™ SLs interface emulator supports LCS AP protocol messages and LPP payload protocols required for simulating E-SMLC and MME network elements over SLs interface. MAPS™ SLs emulator supports UE based positioning method (A-GNSS) in LTE network.
Recently, one of the major defence, and security agency requested for E-SMLC node simulator supporting A-GNSS location information, using LPP payload protocol over LCS AP. MAPS™ SLs interface emulator supported their test requirements by simulating all location service procedures expected between E-SMLC and MME, thus testing their MME node for complete functionality.
Customers need test methodologies that will allow them to benchmark real-world positioning performance of devices. Within the core network, this requires testing of E-SMLC and MME entities.
MAPS™ SLs emulator supports such test requirements by simulating all location service procedures between E-SMLC and MME using UE based A-GNSS positioning method, thus testing either or both entities for all probable scenarios.
MAPS™ E-SMLC seamlessly interacted with customer’s real-time MME requesting the current location of a subscriber by initiating LPP location requests on LCSAP sessions.
MAPS™ SLs supports following LCS-AP interface procedures:
- Location Service Request - The MME sends an LCS-AP Location Request message to the E-SMLC associated with the current serving cell for the target UE to obtain the location estimate for a target UE in E-UTRAN.
- Location Information Exchange - purpose is two-way transfer of LPP messages between an E-SMLC and a MME. Following are the supported LPP procedures:
- Request Capabilities (E-SMLC → UE)
- Provide Capabilities (UE → E-SMLC)
- Request Location Information (E-SMLC → UE)
- Provide Location Information (UE → E-SMLC)
- LPP Abort
- LPP Error
- LPP ack
- Location Abort procedure - procedure is used by one endpoint to notify the other endpoints to abort an ongoing procedure.
- Reset procedure - procedure enables an E-SMLC or an MME that has undergone a failure with loss of location service transactions to indicate this to a partner entity. The recipient entity can then release its own connection and transaction resources.
Shown below is a typical message flow on SLs interface procedure between MME and E-SMLC:
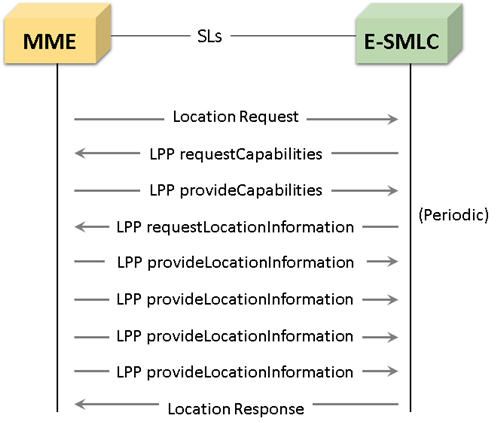
LTE SLs interface procedure
The same procedure realized by MAPS™ SLs emulator when configured as E-SMLC node is shown in the figure below.
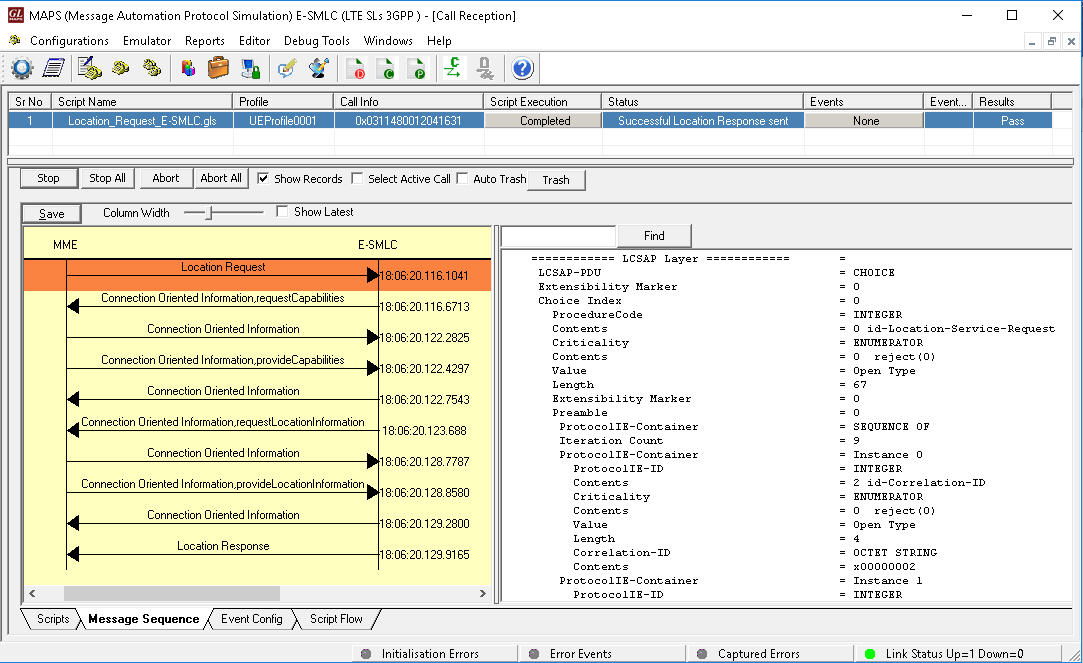
MAPS™ SLs (E-SMLC) simulating SLs interface procedure
Apart from the above SLs interface procedure simulation, MAPS™ SLs also supports following additional capabilities -
- Error Simulation: MAPS™ also supports few error simulation scenarios to send invalid responses – TimeOut, Location Error, LPP Abort, LPP Error. Apart from these, user events are also available within the scripts to send LPP Error / Abort whenever required.
 Back to Newsletter Index Page
Back to Newsletter Index Page