GL Announces Comprehensive Codec Support for Telecom Networks
Welcome to another June, 2016 issue of GL Communications' Newsletter providing information and insight into our supported Voiceband Codecs for TDM, VoIP and Wireless Products.
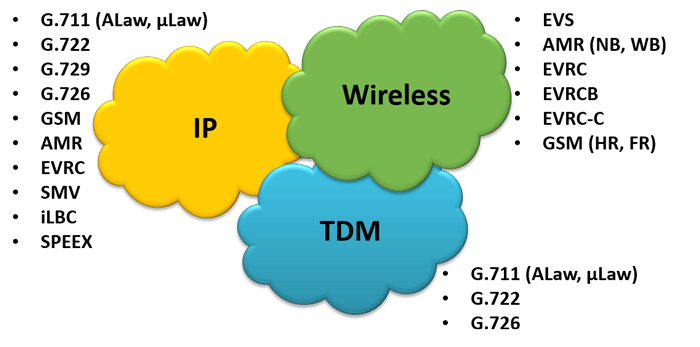
Overview
The word "codec" is a compression of the two words "coder decoder" and is used to identify a voice compression algorithm. Engineers are always looking to transmit or store voice in the least bandwidth and time - thus the need for more sophisticated codecs. Applications include:
- Wireless networks where efficient use of scarce frequency spectrum is important
- VoIP networks where packetized and compressed voice is used to transmit over the World Wide Web
- PCs, MP3 players, and mobile phones where codecs are used to store and play music
GL Products Support Almost ALL CODECS
- µ-Law, A-law (G.711)
These versions of PCM (Pulse Code Modulation) have been the standard throughout the world for digital voice transmission for telephony since early 1960’s. Voice is filtered between 300 to 3400 Hz, then sampled at 8000 samples/second, with 12 to 13 bits per sample, then companded to 8 bits/sample resulting in 64 kbps. The two algorithms defined in the standard (G.711) are µ-Law (North America & Japan) and A-law (used in Europe and the rest of the world).
- G.726 (40kbps, 32kbps, 24kbps, 16kbps)
This is Adaptive Differential Pulse Code Modulation (ADPCM). Originally, a half-rate alternative to ITU-T G.711 and includes both the G.721 and G.723 standards. G.726 compresses by converting between linear, A-law (used in Europe) or µ-Law (used in the U.S and Japan) PCM and 40, 32, 24 or 16 kbps.
- G.729, G.729B
G.729 operates at a bit rate of 8 kbps with an encoding frame length of 10 ms and 5 ms look ahead, but there are extensions, that are normally presented as G.729a and G.729b. Annex A is a low-complexity version of the G.729 standard. Annex B defines Voice Activity Detection (VAD)/Comfort Noise Generator (CNG) /Discontinuous Transmission (DTX) for G.729 and G.729A.
- GSM (HR, FR, EFR)
GSM-FR is a Full Rate speech coder standardized by the ETSI to compressing toll quality speech (8000 samples / second) and it was the first digital speech coding standard used in GSM digital mobile phone systems. The coder has a bit rate of 13 kbps with an encoding frame length of 20 ms. The coder works on a frame of 160 speech samples with an encoding frame length of 20 ms, and look ahead is not required.
GSM-EFR (6.60) is an extended version of GSM-FR (6.10) codec. With sampling frequency of 8000 samples/sec and frame size of 31 bytes, it achieves the bit rate of 12.2 kbps with an encoding fixed frame length of 20 ms. It supports VAD that helps saving bandwidth.
GSM HR 6.20 operates with sampling frequency of 8000 samples/sec. It outputs the frames of size 14 Bytes, that puts the bit rate of encoder at 5.6kbps with an encoding frame length of 20 ms. The GSM HR Codec also supports VAD to allow saving of bandwidth.
- Adaptive Multi-Rate Speech Codec (AMR) (AMR Narrow Band (NB), AMR Wide Band (WB))
AMR is the 3GPP standard codec for narrowband speech and multimedia messaging services over GSM and evolved GSM (WCDMA, GPRS and EDGE) networks. It is designed to provide transcoder free connectivity between GSM, US-TDMA and Personal Digital Cellular (PDC) networks, which is currently used only in Japan. AMR operates at eight bit rates in the range of 4.75 to 12.2 kbps with an encoding frame length of 20 ms and it was specifically designed to improve link robustness.
AMR-WB provides improved speech quality because of a wider speech bandwidth that is of 50–7000 Hz compared to narrowband speech coders which in general are optimized for POTS wireline quality of 300–3400 Hz.
- Selectable Mode Vocoder (SMV)
The SMV codec compresses each 20 milliseconds of 8000 Hz, 16-bit sampled speech input into output frames of one of the four different sizes: Rate 1 (171 bits), Rate 1/2 (80 bits), Rate 1/4 (40 bits), or Rate 1/8 (16 bits) with an encoding frame length of 20 ms. SMV is the preferred speech codec standard for CDMA2000, and also used in third generation handsets.
- Internet Low Bit Rate Codec (iLBC)
The iLBC codec is suitable for real time communications such as, telephony and video conferencing, streaming audio, archival and messaging. The iLBC codec is an algorithm that compresses each basic frame (20 ms or 30 ms) of 8000 Hz, 16-bit sampled input speech, into output frames with rate of 400 bits for 30 ms basic frame size and 304 bits for 20 ms basic frame size. The codec supports two basic frame lengths: 30 ms at 13.33 kbit/s and 20 ms at the rate 15.2 kbit/s, using block independent linear-predictive coding (LPC) algorithm.
- SPEEX (Narrow Band (NB), Wide Band (WB))
SPEEX NB is based on CELP Narrowband (8 kHz with an encoding fixed frame length of 20 ms) open source codec specifically used for VoIP and file-based applications.
SPEEX WB has a sampling rate of16000 samples/sec with an encoding fixed frame length of 20 ms, which makes it a wide band codec.
- G722, G722.1
G.722 is a wideband speech codec standard operating at 48, 56 and 64 kbps with an encoding frame length of 10 ms. It is derived based on sub-band ADPCM (SB-ADPCM). G.722 samples audio data at a rate of 16 kHz (using 14 bits) with an encoding frame length of 10 ms, double that of traditional telephony interfaces, that provides superior audio quality with clarity.
- Enhanced Variable Rate Codec (EVRC), EVRC-B, EVRC-C
EVRC CODEC is a speech codec used in CDMA networks. It was developed to replace the Qualcomm code-excited linear prediction (QCELP) vocoder that consumed more bandwidth on the carrier's networks. It was developed to offer the mobile carriers increased capacity on their networks with lesser bandwidth usage or wireless spectrum.
EVRC-B is an enhancement to EVRC and compresses each 20 milliseconds of 8000 Hz, 16-bit sampled speech input into output frames of one of the four sizes: Rate 1 - 171 bits, Rate 1/2 - 80 bits, Rate 1/4 - 40 bits, Rate 1/8 - 16 bits. Important enhancement in EVRC-B is the use of 1/4 rate frames that were not used in EVRC. This provides lower average data rates (ADRs) compared to EVRC, for a given voice quality. EVRC-C adds the feature of encoding wideband signals sampled at 16 kHz with signal bandwidth up to 7 kHz.
- Enhanced Voice Services Codec (EVS)
EVS provides vastly improved voice quality, network capacity and advanced features for voice services over LTE and other radio access technologies standardized by 3GPP. It is the first 3GPP conversational codec providing up to 20 kHz audio bandwidth, offering speech quality that of highest standard.
EVS codec includes a multi-rate audio codec, a source controlled variable bit-rate (SC-VBR) scheme, a VAD, a comfort noise generation (CNG) system, and an error concealment (EC) mechanism to offset the effects of transmission errors resulting in lost packets. Its channel-aware mode feature further improves frame/packet error resilience.
- Voice Quality Measurement: R-Factor / MOS
E-Model based Mean Opinion Scores (MOS) and R-Factor score are two commonly used methods to measure the quality of voice over IP network. The MOS uses ITU-T G.107 E-Model and is based on a subjective method of calculation to assess voice quality.
R-Factor is a non-intrusive voice quality rating factor based on the quality of packet flows. Its voice quality score is based on various network parameters, including codec type, packet loss, packet jitter, and packet delay.
GL Communications products support a variety of signaling and audio processing applications. Using these tools, one can emulate, analyze, and troubleshoot audio signaling over TDM, IP and Wirelss Platforms. Each of these tools support the narrow-band, and wideband (HD audio) codec standards. For more details, users can refer to the supported CODECS webpage.
 Back to Newsletter Index Page
Back to Newsletter Index Page