Newsletter: GL Announces Emulation of 3G Protocols Over IP
Welcome to our November 2011 issue of GL's Newsletter. Today we introduce our new product "Emulation of 3G Protocols over IP".
The transition to an all IP infrastructure is not necessarily waiting for LTE (4G). Carriers are building out their 3G networks opting for IP (Internet Protocol) over ATM (Asynchronous Transfer Mode) in the core network as well as the Radio Access Network (RAN). Although ATM was the original transport / switching methodology recommended by standards bodies for 3G, it's been widely accepted that IP is more flexible and economical in accommodating a mix of traffic (voice, video, and data) while providing almost equal performance for real time traffic, e.g. voice. IP provides much better link utilization for heavily loaded last mile links (Node B to RNC - so called "backhaul links").
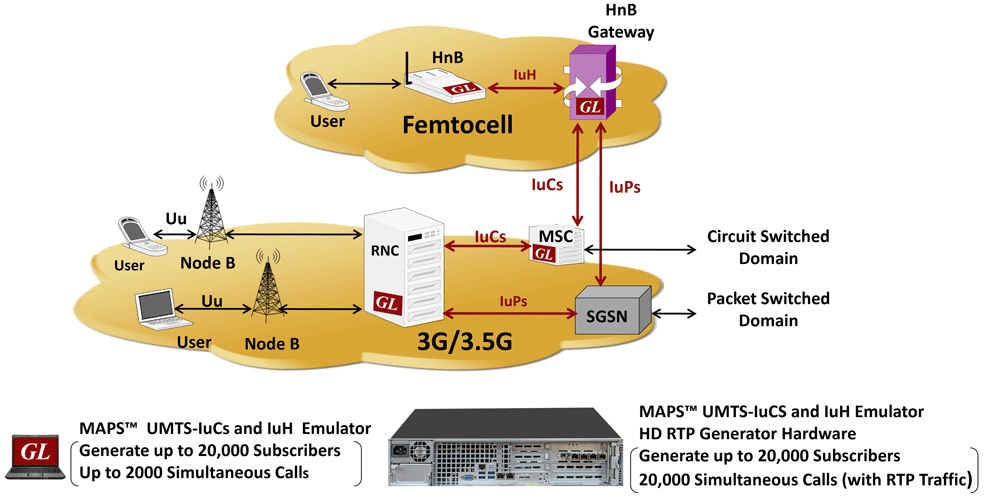
Our latest product emulates all elements involved in the IuCS and IuH interfaces, namely the RNC, MSC, Home NodeB (HnB - Femtocell), and Home NodeB (HnB) Gateway.
Introduction
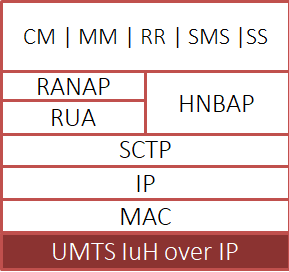
Universal Mobile Telecommunications System, or UMTS, is a 3rd generation mobile technology evolved from GSM (2nd generation) technology. It uses WCDMA (Wideband CDMA) as the radio access technology. With increased spectral efficiency and higher bandwidth, the UMTS network can support greater data rates as well as voice and video to wireless end users. The underlying transport layer for UMTS can be Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM), or Internet Protocol (IP).
IP based UMTS supports integrated services such as multimedia and global roaming to mobile users. The IP based UMTS network consists of the following elements:
- NodeB - supporting broadband mobile users
- Radio Network Controller (RNC) - manages radio resources (NodeBs) and routes traffic to circuit and packet switched elements
- Mobile Switching Center (MSC) - circuit switching element for voice
- Serving GPRS Support Node (SGSN) - packet switching element for data and video
- Femto Home NodeB (Femto Cell) - for enhanced coverage indoors and to offload the radio access network
- Femto Home NodeB Gateway (HnB-GW) - provides wired broadband interface
To emulate the various components of UMTS, GL utilizes its MAPS foundation architecture - a versatile platform for detailed emulation of a wide variety of protocols. MAPS™ supports emulation of many protocols like ISDN, SS7, GSM, LTE, SIP, Megaco, MGCP, SIGTRAN, and many others.
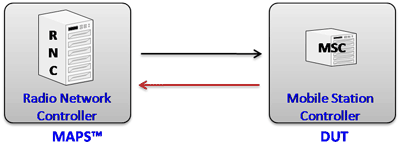
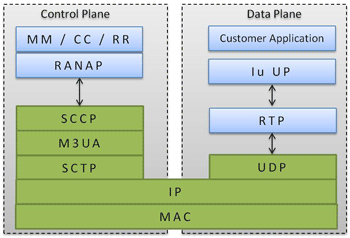
GL's Message Automation & Protocol Simulation (MAPS™) designed for UMTS IuCS interface can emulate the RNC (Radio Network Controller) and the MSC (Mobile Switching Center) by generating RANAP and DTAP signaling messages over SCTP.
Where RANAP and DTAP are:
RANAP - is a control plane protocol (Iu interface) between RNC (Radio Network Controller) and CN (Core Network) in the UMTS stack.
DTAP - is a layer 3 protocol between the MSC (Mobile Switching Center) and the MS (Mobile Station).
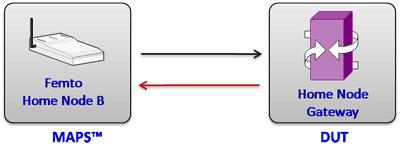
GL's Message Automation & Protocol Simulation (MAPS™) designed for UMTS IuH interface can simulate Femto Home Node B (HnB), and a Femto Home Node Gateway (HnB-GW) by generating RANAP signaling messages over SCTP as Transport layer. A femtocell is a small cellular base station designed for use in residential or small business environments. Femtocells can offload the RAN and provide better coverage, plus improved data download & upload speeds. IuH links Femto Access Point (HNB) and a Femto Gateway (HNB-GW).
MAPS™ also supports RTP traffic simulation (requires additional licensing) over UMTS-IuCS and UMTS-IuH interfaces. RTP traffic simulation supports the following actions for almost all standard codecs.
- Transmitting Voice Files
- Transmitting DTMF, MF Digits, and other Tones and Dual Tones
- Recording Voice Files
- Monitoring Single and Dual Tones, DTMF and MF digits
- Loopback, Talk using Microphone, Play to Speaker
MAPS™ UMTS IuCS and IuH Emulator Specifics
Important Features
- Simulates MSC, RNC, HNB, and HN GW entities
- Generates and process all Mobility Management, Session Management, RANAP, and DTAP messages
- User controlled access to RANAP, and DTAP messages
- Ready scripts for Mobile Originating, Mobile Terminating, Location Updating procedures for quick testing
- Supports Authentication, TMSI Reallocation, Encryption, and other optional procedures
- Provides fault insertion, and erroneous call flows testing capability.
- Impairments can be applied to messages to simulate error conditions
- Supports RTP traffic generation and reception (requires additional license)
- Supported Codecs:
- G.711 (A-law / Mu-law - 64kbps), G.711 App II (ALaw and MuLaw with VAD Support), G.729, G.729B (8 kbps), G.726 (5 bit 40 kbps/4 bit 32 kbps/3 bit 24 kbps/2 bit 16 kbps), G726 (40/32/24/16 kbps with VAD), GSM (13.2 kbps)
- AMR (4.75, 5.15, 5.9, 6.7, 7.4, 7.95, 10.2, & 12.2 kbps) (optional codec)
- AMR_WB
- EVRC (Rates - 1/8, ½ and 1) , EVRC0 (optional codec), EVRC_B (Rates - 1/8, ¼, ½, and 1), EVRC_B0 (optional codec),EVRC_C
- SMV (Modes - 0, 1, 2 and 3- Available if licenses are provided or owned, please call GL)
- iLBC (for 20msec), iLBC_13_33 (for 30msec)
- SPEEX, G722, G722.1, SPEEX_WB, iSAC (optional codec)
- Supports customization of call flows and message templates using Script editor and Message editor.
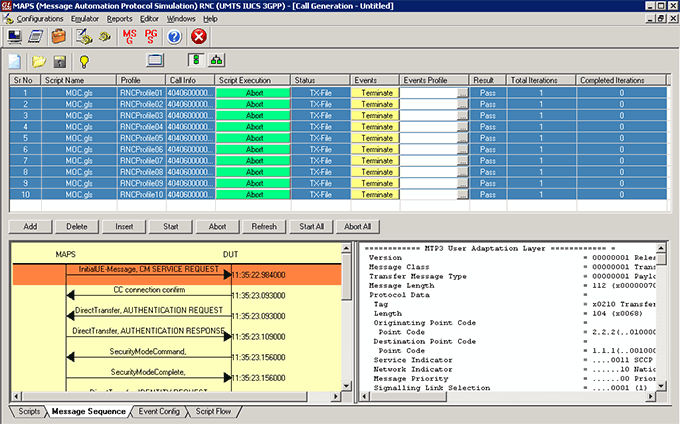
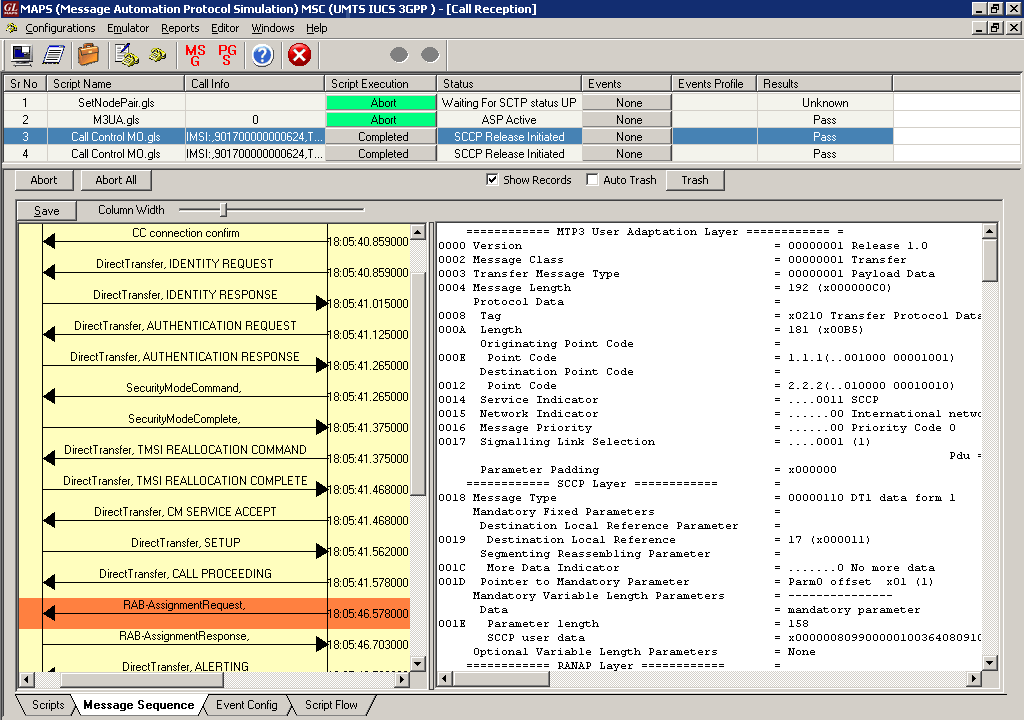
- Supports scripted call generation and automated call reception.
- Provides protocol trace with full message decoding, and graphical ladder diagrams of call flow with time stamp
- Script based & protocol independent software architecture.
- Provides call statistics and associated captured events and error events during call simulation.
Call Generation and Call Reception
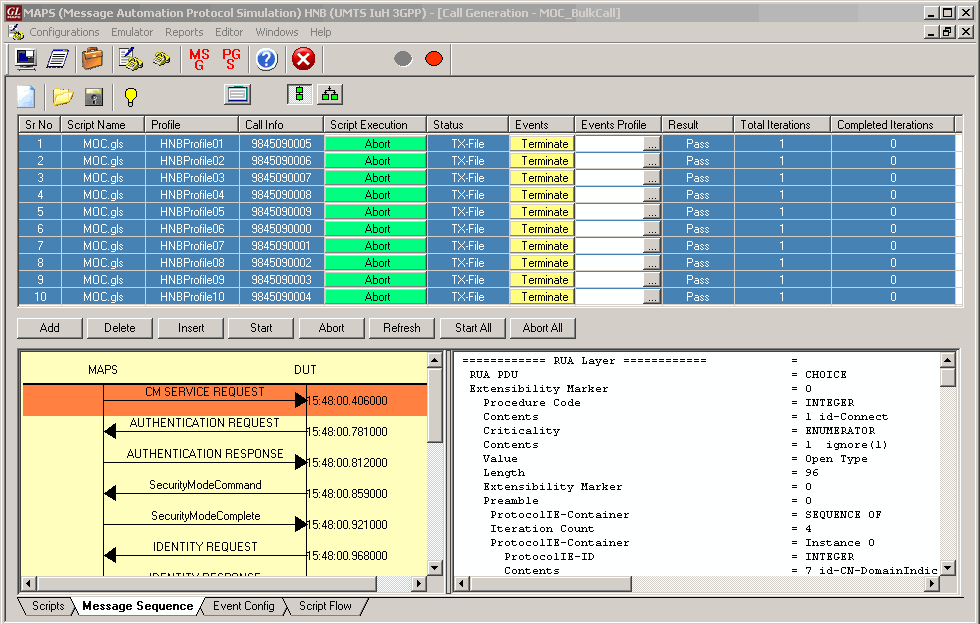
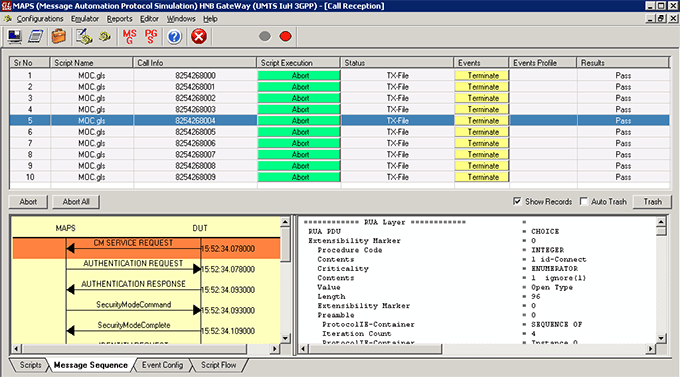
Call Generation option allows the user to simulate outgoing communications where an outgoing call is initiated by sending call control messages using proper scripts and profiles. The profile allows necessary parameters of call control messages to be changed during runtime. Messages are exchanged between the MAPS™ and the DUT. MAPS™ application acts as either the Caller or resides at the network terminal acting as Callee.
Call generated from other entity can be automatically detected in call reception window by pre-setting the required scripts in the Incoming Call Handler window.
IuCS interface
In IuCS interface, MAPS™ acts as either RNC to test MSC (DUT) or MSC to test RNC (DUT) and simulates the following call flow scenarios:
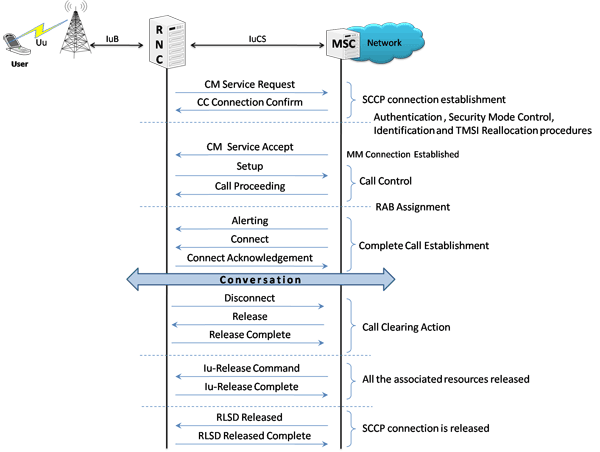
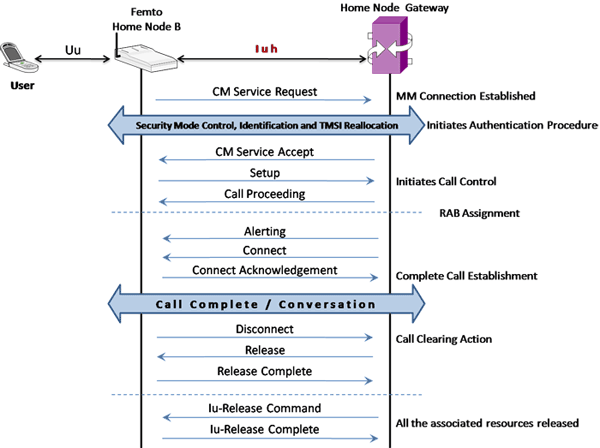
- Mobile Originating Call (MOC) - The MOC call is initiated by the user equipment (UE). On receiving the CM Service Request message from UE, the network initiates authentication procedures. After the authentication procedures, the request is accepted and the Call Control procedures will start and the call is established.
- Location Updating (LU) - Whenever mobile station (MS) moves out of its location to a new location then it needs to inform the network about its new location. The UE initiates the call by sending location update message to network. And on receiving acknowledgment, the LU call gets terminated.
- Mobile Terminating Call (MTC) - The MTC is initiated by Network by sending Paging message towards UE. Here, the UE is the receiver of a call. UE will send the Paging Response message. The rest of the call flow is same as a MOC call.
As an illustration, the Mobile Originating Call (MOC) Flow on IuCS Interface is explained below.
IuH interface
In IuH interface, MAPS™ acts as either HNBGW to test HNB (DUT) or as HNB to test HNB GW (DUT) simulates the following call flow scenarios:
- Mobile Originating Call (MOC)
- Location Updating (LU)
- Mobile Terminating Call (MTC)
As an illustration, the Mobile Originating Call (MOC) Flow on IuH Interface is explained below.
Load Generation Testing
MAPS™ supports Bulk Call Simulation and Stress/Load Testing capabilities through Load Generation feature. Load Generation window helps users configure Stress/Load Testing parameters such as Call per second (CPS) or Busy hour call attempts (BHCA), Max Simultaneous Calls and Burst parameters
For comprehensive information on the application, please visit UMTS IuCS and IuH emulation over IP web page.
 Back to Newsletter Index Page
Back to Newsletter Index Page