Enhanced UMTS IuCS and IuH with Iu-UP Protocol Support
Welcome to another April 2014 issue of GL's Newsletter providing information and insight into our enhanced MAPS™ UMTS IuCS and IuH Interface Emulator with Iu-UP protocol layer of the Radio Network that is used to convey user data associated with Radio Access Bearers (RABs).
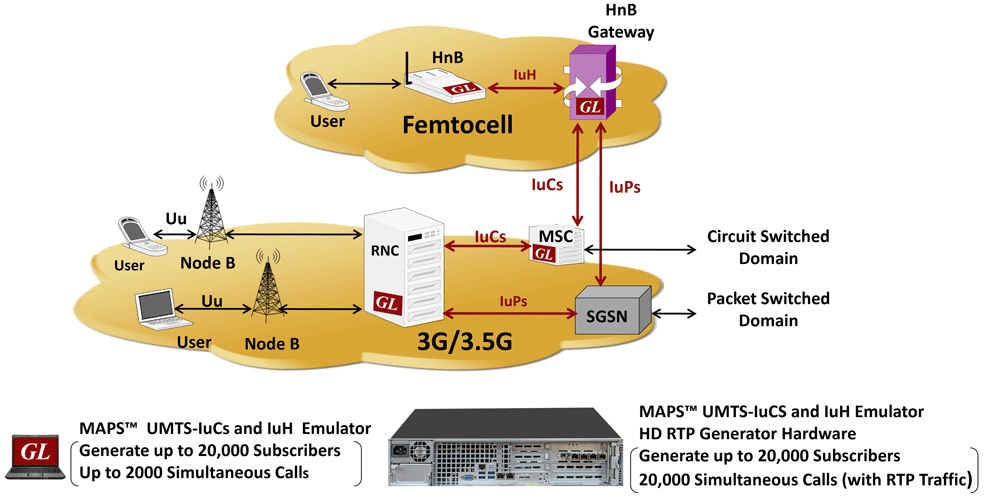
Overview
MAPS™ UMTS IuCS can emulate the IuCS interface between the RNC (Radio Network Controller) and the MSC (Mobile Switching Center) nodes, and MAPS™ UMTS IuH interface can emulate IuH interface between the Femto Home Node B (HnB), and a Femto Home Node Gateway (HnB-GW) by generating RANAP and DTAP signaling messages over SCTP. Both emulators support all standard protocols required for the accurate UMTS interfaces emulation. As an enhancement, GL has added the Iu-UP protocol support to this existing protocol stack as shown in the figure below.
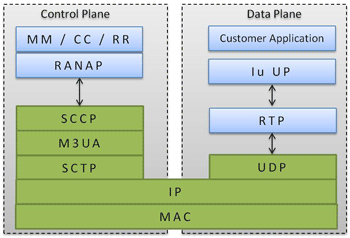
UMTS IuCS with User Plane Protocol Stack
The Iu-UP protocol layer of the Radio Network is used to convey user data associated with Radio Access Bearers (RABs). The Iu-UP protocol operates in two modes: Transparent Mode and Support Mode. The core network chooses the mode of operation according to the service/application requirements.In Transparent Mode, information is transferred without any processing, for example, the transfer of GTP-U PDUs across the Iu interface.
In Support Mode, the core network creates a task to transfer additional feature along with the ordinary user data. For example, the RTP traffic (AMR payload part) is carried over Iu-UP in Support Mode. The possible functions in Support Mode are Transfer of User Data, Initialization, Rate Control, Error handling, Time alignment, and Frame- quality classifications.
MAPS™ IuCS emulator has been enhanced to support Iu-UP (Iu User Plane Interface) with additional licensing to carry RTP traffic (AMR payload part) over Iu interface in support mode of operation for predefined SDU size. The RAB assignment procedure in RANAP will give the AMR codec rates to be used for this particular session. The conversational speech Radio Access Bearer (RAB) is tailored to Adaptive Multi Rate (AMR) speech and will also be used to carry emergency calls.
Additionally, MAPS™ IuCS also supports Auto and User-defined RTP traffic simulation over normal RTP sessions with additional RTP Core licensing. RTP traffic simulation supports the following actions for almost all Standard Codec.
- Transmitting Voice Files
- Transmitting DTMF, MF Digits, and Single and Dual Tones
- Recording Voice Files
- Monitoring Single and Dual Tones, DTMF, and MF digits
- Loopback, Talk using Microphone, Play to Speaker
Supported Protocols
| Supported Protocols | Specification Used |
|---|---|
| IuCS Interface | |
| SCCP | Q.713, CCITT (ITU-T) Blue Book |
| MTP3 | Q.704, ITU-T Blue Book |
| RANAP | 3GPP TS 25.413 V9.1.0 |
| MM / CC | 3GPP TS 24.008 V5.16.0 (2006-06) |
| RR | 3GPP TS 04.18 V8.13.0 |
| SMS | 3GPP TS 03.40 V7.5.0 & 3GPP TS 04.11 V7.1.0 GSM 03.38 version 7.2.0 Release 1998 |
| Iu-UP | 3GPP TS 25.415 |
| IuH Interface | |
| RUA | 3GPP TS 25468 V9.1.0 |
| RANAP | 3GPP TS 25.413 V9.1.0 |
| MM / CC | 3GPP TS 04.08 V7.17.0 |
| RR | 3GPP TS 04.18 V8.13.0 |
| SMS | 3GPP TS 03.40 V7.5.0 & 3GPP TS 04.11 V7.1.0 GSM 03.38 version 7.2.0 Release 1998 |
Important Features
- Simulates RNC, MSC, Home NodeB (HnB) and Home NodeB Gateway (HN GW) entities
- Generates and process all Mobility Management, Session Management, RANAP and DTAP messages
- User controlled access to RANAP, and DTAP messages
- Ready scripts for Mobile Originating, Mobile Terminating, Location Updating procedures for quick testing
- Supports RAB Assignment, Authentication, TMSI Reallocation, Encryption, and other procedures
- Provides fault insertion, and erroneous call flows testing capability
- Impairments can be applied to messages to simulate error conditions
- Supports RTP traffic over Iu-UP protocol and also over normal RTP sessions (requires additional licenses)
- Supported Codecs: AMR & AMR-WB
- Supports customization of call flows and message templates using Script editor and Message editor
- Supports scripted call generation and automated call reception
- Provides protocol trace with full message decoding, and graphical ladder diagrams of call flow with time stamp
- Script based & protocol independent software architecture
- Provides call statistics and associated captured events and error events during call simulation.
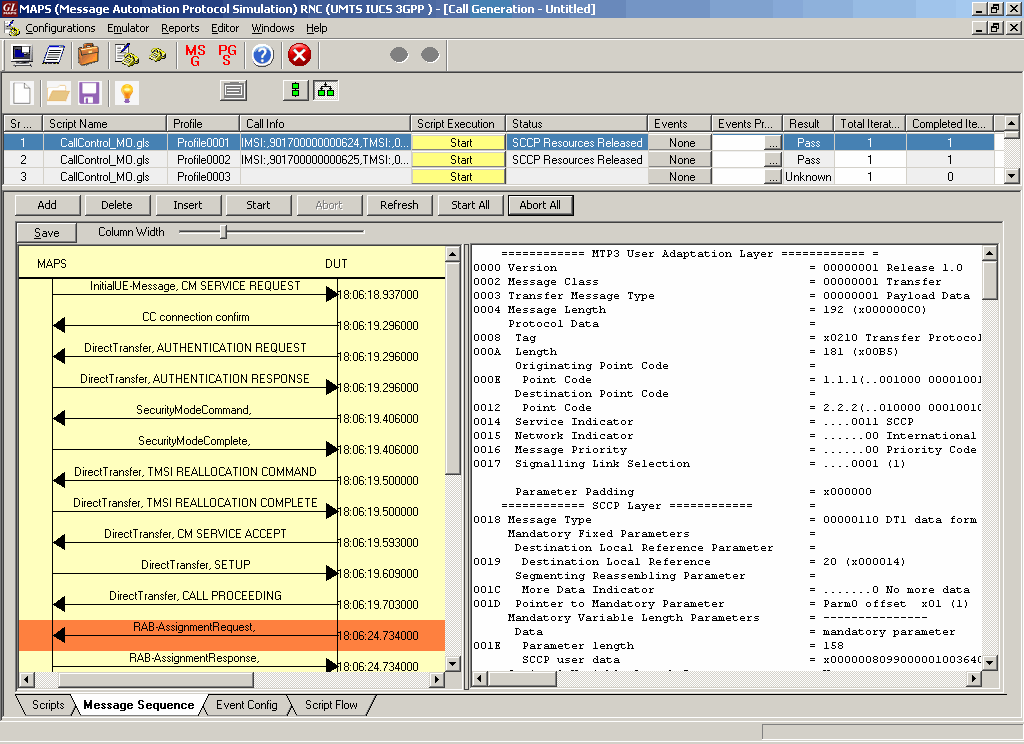
Call Generation and Call Reception
Call Generation option allows the user to simulate outgoing communications where an outgoing call is initiated by sending call control messages using proper scripts and profiles. The profile allows necessary parameters of call control messages to be changed during runtime. Messages are exchanged between the MAPS™ and the DUT. MAPS™ application acts as either the Caller or resides at the network terminal acting as Callee.
Call generated from other entity can be automatically detected in call reception window by pre-setting the required scripts in the Incoming Call Handler window.
IuCs interface
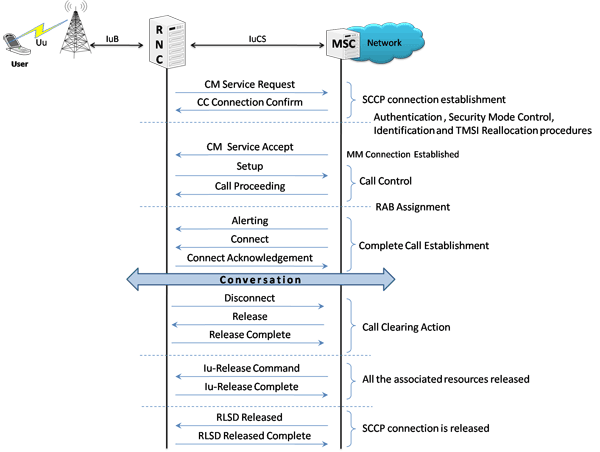
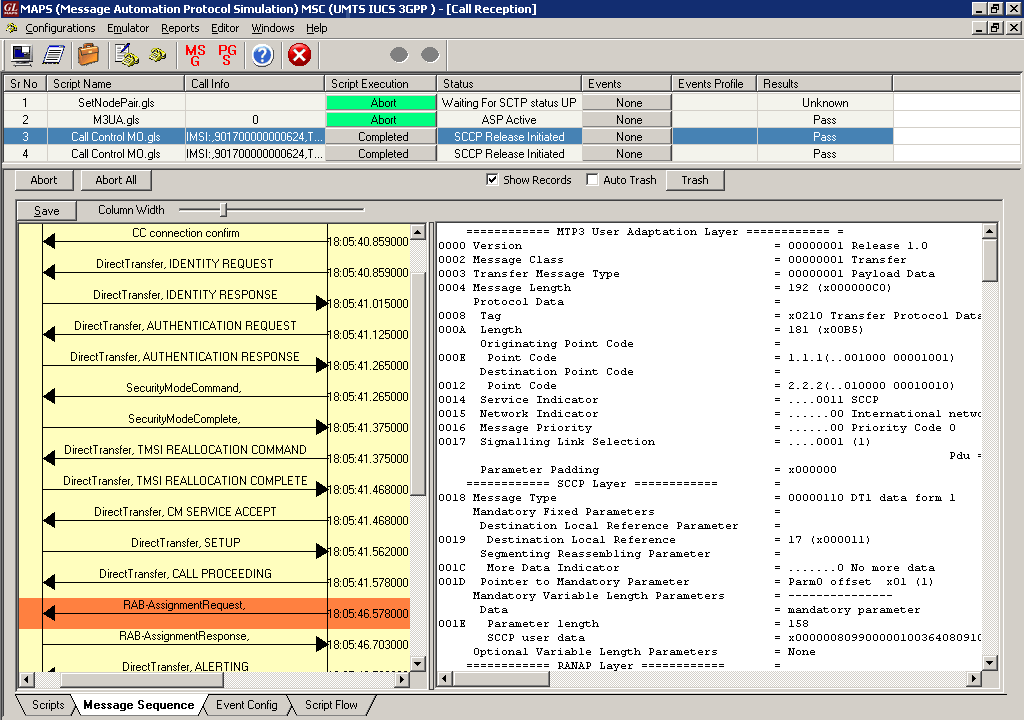
In IuCs interface, MAPS™ acts as either RNC to test MSC (DUT) or MSC to test RNC (DUT) and simulates the following call flow scenarios:
As an illustration, the Mobile Originating Call (MOC) Flow on IuCs Interface is explained below.
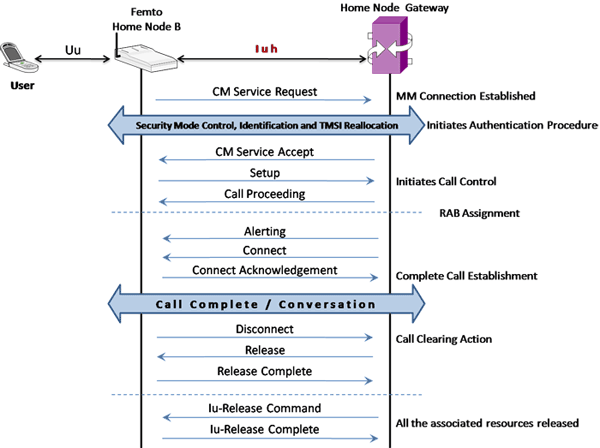
IuH interface
In IuH interface, MAPS™ acts as either HNBGW to test HNB (DUT) or as HNB to test HNB GW (DUT).
As an illustration, the Mobile Originating Call (MOC) Flow on IuH Interface is explained below.
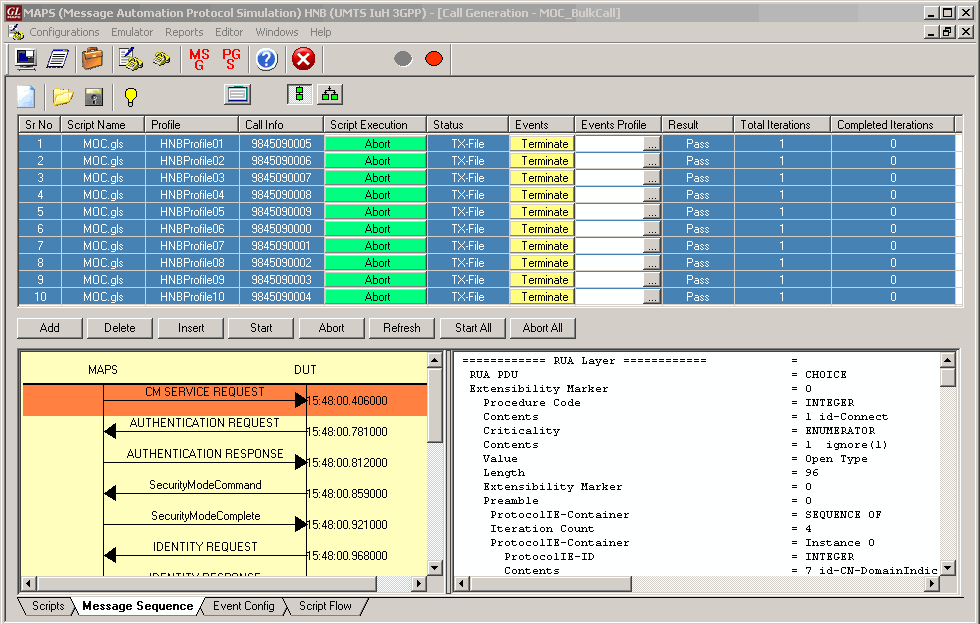
Load Generation Testing
MAPS™ supports Bulk Call Simulation and Stress/Load Testing capabilities through Load Generation feature. Load Generation window helps users configure Stress/Load Testing parameters such as Call per second (CPS) or Busy hour call attempts (BHCA), Max Simultaneous Calls and Burst parameters.
 Back to Newsletter Index Page
Back to Newsletter Index Page